Wind Energy has been the first renewable energy source discovered by man. In the past, wind energy was immediately used on site as motive power for industrial and pre-industrial applications, such as the wind mills.
Nowadays this source’s potential provides for clean energy production is much more extensively used through the setting up of the so-called Wind Farms.
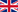
A wind farm is made of several turbines (aerogenerators) converting wind’s kinetic energy into electric energy. This conversion is based on a very simple principle: wind activates the rotor, usually with two or three blades, connected to a transformer included in the vessel; rotation is transmitted to a mechanic system, a rotations multiplier gearbox and it is converted into electricity by the transformer and conveyed in the network together with the one produced by the other turbines. The big-sized wind turbines are tubular steel towers in a range from 40 to 130 mt tall, because at that height they can catch winds 3 or 4 times stronger than those blowing at sea level.
It is also possible to install wind turbines in the sea through floating system anchored to the sea bottom. The Wind Farms in the sea are called “ off-shore wind farms” and they are usually mounted some miles away from the coasts to mitigate the visual pollution and because winds can be stronger over water than on the coast. The worldwide wind energy market is significantly growing, especially because, rated power being equal, wind Energy is among the cheapest to produce.